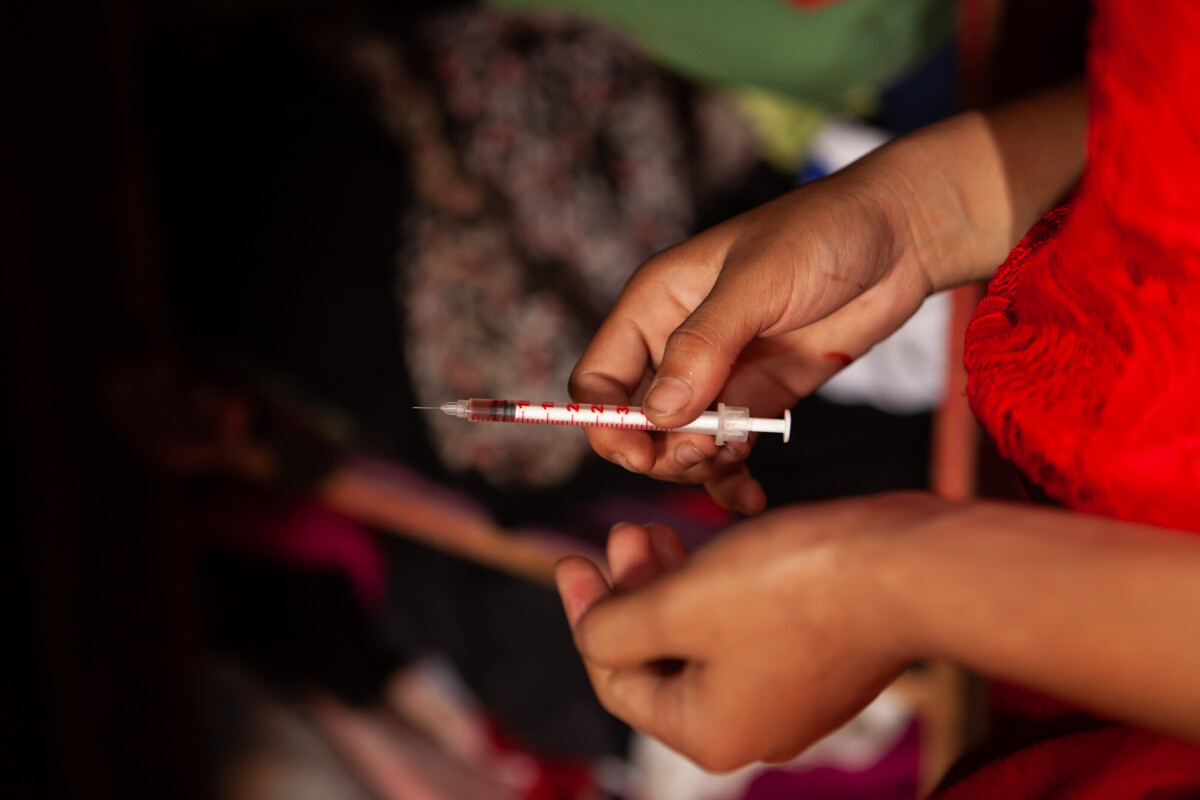
Smaller reservoir
Lower risk
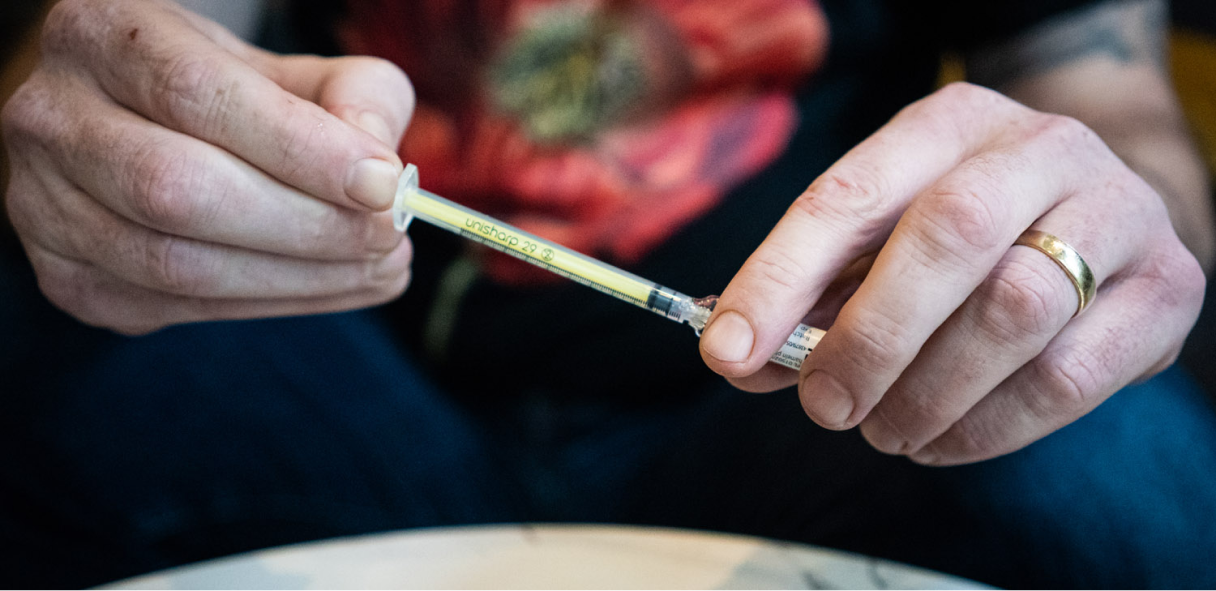
Harm reduction is a public health approach that aims to reduce the harm associated with drug use or other high-risk habits. Some examples include needle exchange programs, safe injection sites and low dead space syringes, among many others.
Low dead space syringes have less space between the needle and the plunger when it’s fully pushed down, compared to traditional syringes. This ‘dead space’ is where blood typically pools in a syringe, which is one of the ways infections such as hepatitis and HIV can be transmitted from one person to another when needles and syringes are shared. By limiting this reservoir of blood, these syringes could help limit infectious disease transmission.
Though people who inject drugs represent just 10% of the 58 million people infected with hepatitis C worldwide, injection drug use contributes to 43% of all new infections. Limiting continued transmission of the virus among people who inject drugs is critical to combating hepatitis C globally.
Building off previous work that advanced rapid hepatitis C tests, showed that hepatitis C can be diagnosed and cured in lower-level health settings and helped bring down the cost of care, we are now supporting better integration of hepatitis C testing and treatment within harm reduction programs, with a focus on reaching the populations where the rates of infections are highest.
Related publications
ISSUE BRIEF